INTRODUCTION
Habitats Reclaimed explores the fascinating process of reclaiming habitats that have been damaged or altered by human activities. This article delves into various methods and initiatives aimed at restoring ecosystems to their natural state, highlighting the importance of biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration.
Topic 1
One approach to habitat restoration is reforestation, which involves planting trees in deforested areas to recreate healthy forest ecosystems. Reforestation projects contribute to carbon sequestration, provide wildlife habitats, and help mitigate the effects of climate change.

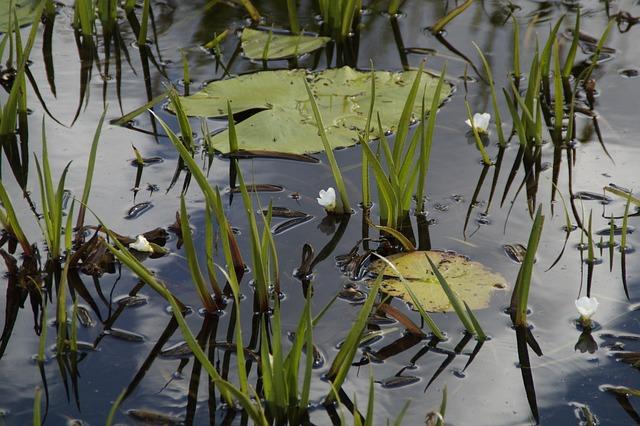
(Image: Pixabay/@AlexCuevasG)
Moreover, wetland restoration plays a crucial role in enhancing water quality, flood control, and supporting diverse plant and animal species. By restoring wetlands, we can improve ecosystem functions and create havens for migratory birds and other wildlife.
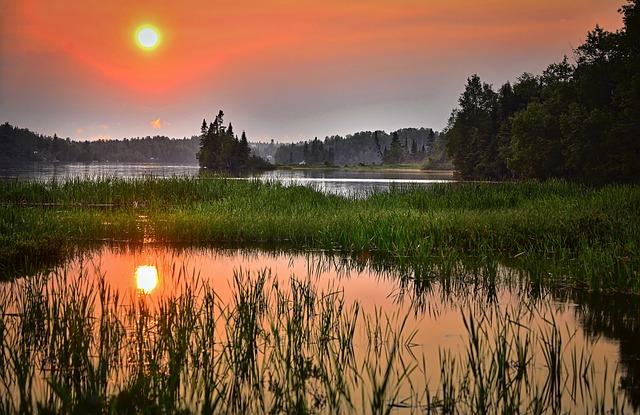

(Image: Pixabay/@AlainAudet)
Collaborative efforts between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and local communities are essential for the success of habitat restoration projects, ensuring long-term sustainability and conservation outcomes.

(Image: Pixabay/@PicsbyAnnyk)
Topic 2
Another aspect of habitat reclamation is marine conservation, focusing on protecting and restoring ocean ecosystems. Marine protected areas, coral reef restoration, and sustainable fishing practices are integral to safeguarding marine biodiversity and preserving delicate underwater habitats.

(Image: Pixabay/@MonicaMaxWest)
Efforts to clean up polluted water bodies and reduce marine debris are vital in maintaining the health of aquatic habitats. Restoring damaged coral reefs and establishing marine reserves help support fish populations, protect endangered species, and promote ecotourism opportunities.
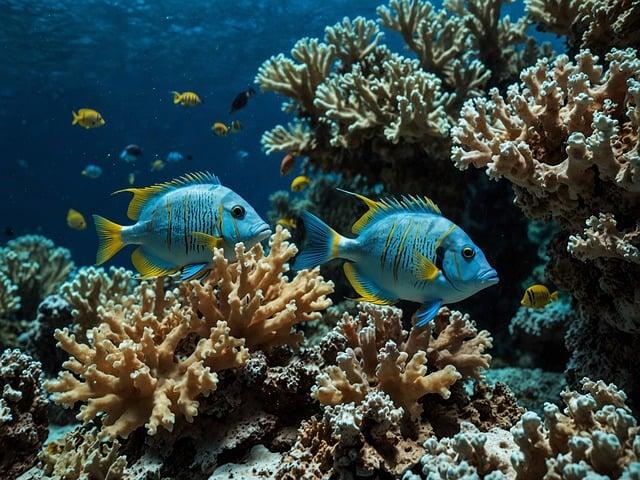

(Image: Pixabay/@Frank_Rietsch)
Education and awareness campaigns play a critical role in engaging the public and fostering a conservation mindset, encouraging sustainable behaviors that benefit marine ecosystems and ensure the long-term well-being of our oceans.

(Image: Pixabay/@ean254)
Topic 3
Urban habitat restoration entails transforming degraded urban spaces into green areas that support biodiversity and provide recreational benefits for city dwellers. Green roofs, community gardens, and urban parks are examples of initiatives that bring nature back into urban environments, improving air quality and urban aesthetics.

(Image: Pixabay/@Pexels)
Incorporating native plant species in urban landscaping enhances pollinator diversity, supports urban wildlife, and creates resilient green infrastructure that helps combat heat island effects and reduce energy consumption. Community involvement in urban greening projects fosters a sense of ownership and pride in local green spaces.

(Image: Pixabay/@Anemone123)
By integrating nature-based solutions into urban planning and design, cities can enhance ecological connectivity, promote biodiversity conservation, and create healthier, more livable urban environments for current and future generations.
(Image: Pixabay/@Macey11)
Topic 4
Restoring degraded agricultural lands through sustainable farming practices like agroforestry, cover cropping, and soil conservation techniques is essential for improving soil health, increasing crop yields, and preserving natural resources. Agroecological approaches that mimic natural ecosystems help reduce reliance on chemical inputs and enhance the resilience of farming systems.

(Image: Pixabay/@RosZie)
Implementing agroforestry systems that combine trees with crops benefits both farmers and the environment by providing additional income sources, improving biodiversity, and sequestering carbon in soil and vegetation. Conservation agriculture practices such as minimum tillage and crop rotation contribute to soil carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
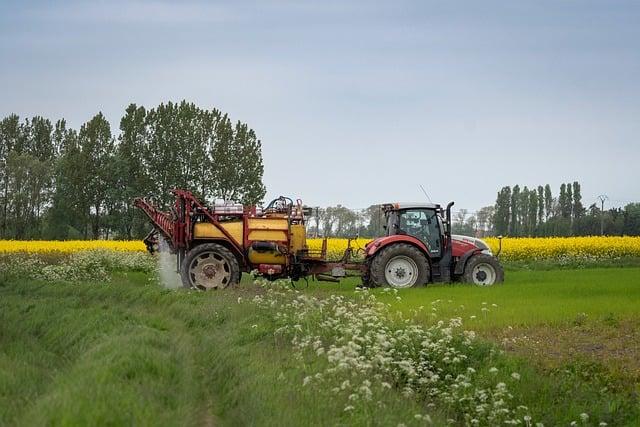

(Image: Pixabay/@dendoktoor)
Promoting sustainable land management practices and supporting smallholder farmers in adopting environmentally friendly techniques are integral to achieving food security, preserving natural habitats, and promoting agrobiodiversity conservation for a more sustainable agricultural future.
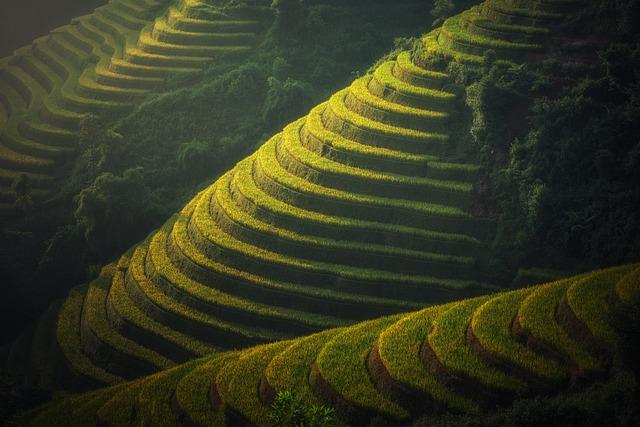

(Image: Pixabay/@sasint)
CONCLUSION
Habitats Reclaimed underscores the significance of restoring and preserving natural habitats to sustain ecosystems and safeguard biodiversity for future generations. Through concerted conservation efforts, we can reclaim degraded habitats, revitalize ecosystems, and create a more harmonious relationship between humans and nature.
FAQs
Q: How can individuals contribute to habitat restoration?
A: Individuals can support habitat restoration by volunteering for conservation organizations, participating in tree-planting events, advocating for sustainable land use practices, and reducing their ecological footprint through conscious consumption choices.
Q: What are the benefits of habitat restoration for biodiversity?
A: Habitat restoration enhances biodiversity by providing suitable habitats for plant and animal species, restoring ecosystem functions, promoting genetic diversity, and increasing resilience to environmental changes, leading to healthier and more robust ecosystems.

